|
|
| (Der Versionsvergleich bezieht 60 dazwischenliegende Versionen mit ein.) |
| Zeile 1: |
Zeile 1: |
| - | '''8.1 The Classification Scheme'''<br/>
| + | ===The Classification Scheme=== |
| | | | |
| | The Danish classification, used since 1996, is the base of the Display® classification schemes. So far the Danish scheme, taking into account a building typology, is the only classification all over Europe.<br/> | | The Danish classification, used since 1996, is the base of the Display® classification schemes. So far the Danish scheme, taking into account a building typology, is the only classification all over Europe.<br/> |
| Zeile 6: |
Zeile 6: |
| | Currently, 11 types of buildings can be classified. The classification scheme could change in the future.<br/> | | Currently, 11 types of buildings can be classified. The classification scheme could change in the future.<br/> |
| | | | |
| - | <u>'''Classification scheme for the primary energy ratio:'''</u><br/> | + | ===<u>'''Classification scheme for the primary energy ratio'''</u>=== |
| | + | [[Image:Classification_for_the_primary_energy_ratio.jpg]]<br/> |
| | | | |
| - | {| align="center" style="background-color:#C0E0F0"
| + | ===<u>'''Classification scheme for the CO2 ratio'''</u>=== |
| - | |-
| + | [[Image:Classification_for_the_CO2_ratio.jpg]]<br/> |
| - | ! scope=col | Class
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | kWh/ (m².yr)
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Day nursery / Kindergarten
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | General school
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Professional school
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Administrative
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Swimming pool
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Sports hall
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Depot
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Social Cultural
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Health Centre
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Rescue Centre
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Multi residential
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | A
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |75 ≤ X
| + | |
| - | |75 ≤ X
| + | |
| - | |75 ≤ X
| + | |
| - | |X ≤ 75
| + | |
| - | |X ≤ 500
| + | |
| - | |X ≤ 75
| + | |
| - | |X ≤ 250
| + | |
| - | |X ≤ 75
| + | |
| - | |X ≤ 250
| + | |
| - | |X ≤ 100
| + | |
| - | |X ≤ 50
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | B
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |75 < X ≤ 145
| + | |
| - | |75 < X ≤ 140
| + | |
| - | |75 < X ≤ 145
| + | |
| - | |75 < X ≤ 140
| + | |
| - | |500 < X ≤ 2000
| + | |
| - | |75 < X ≤ 150
| + | |
| - | |250 < X ≤ 350
| + | |
| - | |75 < X ≤ 160
| + | |
| - | |250 < X ≤ 350
| + | |
| - | |100 < X ≤ 140
| + | |
| - | |50 < X ≤ 100
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | C
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |145< X ≤ 215
| + | |
| - | |140 < X ≤ 205
| + | |
| - | |145< X ≤ 215
| + | |
| - | |140 < X ≤ 205
| + | |
| - | |2000 < X ≤ 3500
| + | |
| - | |150 < X ≤ 225
| + | |
| - | |350 < X ≤ 450
| + | |
| - | |160 < X ≤ 245
| + | |
| - | |350 < X ≤ 450
| + | |
| - | |140 < X ≤ 180
| + | |
| - | |100 < X ≤ 150
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | D
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |215 < X ≤ 285
| + | |
| - | |205 < X ≤ 270
| + | |
| - | |215 < X ≤ 285
| + | |
| - | |205 < X ≤ 270
| + | |
| - | |3500 < X ≤ 5000
| + | |
| - | |225 < X ≤ 300
| + | |
| - | |450 < X ≤ 550
| + | |
| - | |245 < X ≤ 330
| + | |
| - | |450 < X ≤ 550
| + | |
| - | |180 < X ≤ 220
| + | |
| - | |150 < X ≤ 200
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | E
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |285 < X ≤ 355
| + | |
| - | |270 < X ≤ 335
| + | |
| - | |285 < X ≤ 355
| + | |
| - | |270 < X ≤ 335
| + | |
| - | |5000 < X ≤ 6500
| + | |
| - | |300 < X ≤ 375
| + | |
| - | |550 < X ≤ 650
| + | |
| - | |330 < X ≤ 415
| + | |
| - | |550< X ≤ 650
| + | |
| - | |220 < X ≤ 260
| + | |
| - | |200 < X ≤ 250
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | F
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |355 < X ≤ 425
| + | |
| - | |335 < X ≤ 400
| + | |
| - | |355 < X ≤ 425
| + | |
| - | |335 < X ≤ 400
| + | |
| - | |6500 < X ≤ 8000
| + | |
| - | |375 < X ≤ 450
| + | |
| - | |650 < X ≤ 750
| + | |
| - | |415 < X ≤ 500
| + | |
| - | |650 < X ≤ 750
| + | |
| - | |260 < X ≤ 300
| + | |
| - | |250 < X ≤ 300
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | G
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |X > 425
| + | |
| - | |X > 400
| + | |
| - | |X > 425
| + | |
| - | |X > 400
| + | |
| - | |X > 8000
| + | |
| - | |X > 450
| + | |
| - | |X > 750
| + | |
| - | |X > 500
| + | |
| - | |X > 750
| + | |
| - | |X > 300
| + | |
| - | |X > 300
| + | |
| - | |}<br/>
| + | |
| - | '''Table 1: Classification scheme for the primary energy ratio'''<br/> | + | |
| | | | |
| - | <u>'''Classification scheme for the CO2 ratio:'''</u><br/> | + | ===<u>'''Classification for the water ratio'''</u>=== |
| - | {| align="center" style="background-color:#C0E0F0"
| + | [[Image:Classification_for_the_water_ratio.jpg]]<br/> |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Class
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | (kg/ (m².yr)
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Day nursery / Kindergarten
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | General school
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Professional school
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Administrative
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Swimming pool
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Sports hall
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Depot
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Social-Cultural
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Health centre
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Rescue centre
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Multi-residential
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | A
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |15 ≤ X
| + | |
| - | |15 ≤ X
| + | |
| - | |15 ≤ X
| + | |
| - | |15 ≤ X
| + | |
| - | |X ≤ 100
| + | |
| - | |X ≤ 15
| + | |
| - | |X ≤ 50
| + | |
| - | |X ≤ 15
| + | |
| - | |X ≤ 50
| + | |
| - | |X ≤ 20
| + | |
| - | |X ≤ 10
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | B
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |15 < X ≤ 29
| + | |
| - | |15 < X ≤ 28
| + | |
| - | |15 < X ≤ 29
| + | |
| - | |15 < X ≤ 28
| + | |
| - | |100 < X ≤ 300
| + | |
| - | |15 < X ≤ 30
| + | |
| - | |50 < X ≤ 70
| + | |
| - | |15 < X ≤ 32
| + | |
| - | |50 < X ≤ 70
| + | |
| - | |20 < X ≤ 28
| + | |
| - | |10 < X ≤ 20
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | C
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |29< X ≤ 43
| + | |
| - | |28 < X ≤ 41
| + | |
| - | |29< X ≤ 43
| + | |
| - | |28 < X ≤ 41
| + | |
| - | |300 < X ≤ 700
| + | |
| - | |30 < X ≤ 45
| + | |
| - | |70 < X ≤ 90
| + | |
| - | |32 < X ≤ 49
| + | |
| - | |70 < X ≤ 90
| + | |
| - | |28 < X ≤ 36
| + | |
| - | |20 < X ≤ 30
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | D
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |43 < X ≤ 57
| + | |
| - | |41 < X ≤ 54
| + | |
| - | |43 < X ≤ 57
| + | |
| - | |41 < X ≤ 54
| + | |
| - | |700 < X ≤ 1000
| + | |
| - | |45 < X ≤ 60
| + | |
| - | |70 < X ≤ 90
| + | |
| - | |32 < X ≤ 49
| + | |
| - | |70 < X ≤ 90
| + | |
| - | |28 < X ≤ 36
| + | |
| - | |20 < X ≤ 30
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | E
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |57 < X ≤ 71
| + | |
| - | |54 < X ≤ 67
| + | |
| - | |57 < X ≤ 71
| + | |
| - | |54 < X ≤ 67
| + | |
| - | |1000 < X ≤ 1300
| + | |
| - | |60 < X ≤ 75
| + | |
| - | |110< X ≤ 130
| + | |
| - | |56 < X ≤ 73
| + | |
| - | |110< X ≤ 130
| + | |
| - | |44 < X ≤ 52
| + | |
| - | |40 < X ≤ 50
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | F
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |71 < X ≤ 85
| + | |
| - | |67 < X ≤ 80
| + | |
| - | |71 < X ≤ 85
| + | |
| - | |67 < X ≤ 80
| + | |
| - | |1300 < X ≤ 1600
| + | |
| - | |75 < X ≤ 90
| + | |
| - | |130 < X ≤ 150
| + | |
| - | |73 < X ≤ 90
| + | |
| - | |130 < X ≤ 150
| + | |
| - | |52 < X ≤ 60
| + | |
| - | |50 < X ≤ 60
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | G
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |X > 85
| + | |
| - | |X > 80
| + | |
| - | |X > 85
| + | |
| - | |X > 80
| + | |
| - | |X > 1600
| + | |
| - | |X > 90
| + | |
| - | |X > 150
| + | |
| - | |X > 90
| + | |
| - | |X > 150
| + | |
| - | |X > 60
| + | |
| - | |X > 60
| + | |
| - | |}<br/>
| + | |
| - | '''Table 3: Classification scheme for the CO2 ratio'''<br/>
| + | |
| | | | |
| - | <u>'''Classification for the water ratio:'''</u><br/>
| + | ===Conversion Factors and their Sources<br/>=== |
| - | <u>'''Classification scheme for the CO2 ratio:'''</u><br/>
| + | |
| - | {| align="center" style="background-color:#C0E0F0"
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Class
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | (kg/ (m².yr)
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Day nursery / Kindergarten
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | General school
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Professional school
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Administrative
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Swimming pool
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Sports hall
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Depot
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Social-Cultural
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Health centre
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Rescue centre
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Multi-residential
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | A
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |200 ≤ X
| + | |
| - | |100 ≤ X
| + | |
| - | |125 ≤ X
| + | |
| - | |X ≤ 100
| + | |
| - | |X ≤ 80
| + | |
| - | |100 ≤ X
| + | |
| - | |X ≤ 350
| + | |
| - | |X ≤ 50
| + | |
| - | |X ≤ 500
| + | |
| - | |X ≤ 350
| + | |
| - | |X ≤ 500
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | B
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |200 < X ≤ 350
| + | |
| - | |100 < X ≤ 225
| + | |
| - | |125 < X ≤ 250
| + | |
| - | |100 < X ≤ 200
| + | |
| - | |80 < X ≤ 125
| + | |
| - | |100 < X ≤ 225
| + | |
| - | |350 < X ≤ 500
| + | |
| - | |50 < X ≤ 125
| + | |
| - | |500 < X ≤ 750
| + | |
| - | |350 < X ≤ 500
| + | |
| - | |500 < X ≤ 750
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | C
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |350 < X ≤ 500
| + | |
| - | |225 < X ≤ 350
| + | |
| - | |250 < X ≤ 375
| + | |
| - | |200 < X ≤ 300
| + | |
| - | |125 < X ≤ 170
| + | |
| - | |225 < X ≤ 350
| + | |
| - | |500 < X ≤ 650
| + | |
| - | |125 < X ≤ 200
| + | |
| - | |750 < X ≤ 1000
| + | |
| - | |500 < X ≤ 650
| + | |
| - | |750 < X ≤ 1000
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | D
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |500 < X ≤ 650
| + | |
| - | |350 < X ≤ 475
| + | |
| - | |375 < X ≤ 500
| + | |
| - | |300 < X ≤ 400
| + | |
| - | |170 < X ≤ 215
| + | |
| - | |350 < X ≤ 475
| + | |
| - | |650 < X ≤ 800
| + | |
| - | |200 < X ≤ 275
| + | |
| - | |1000 < X ≤ 1250
| + | |
| - | |650 < X ≤ 800
| + | |
| - | |1000 < X ≤ 1250
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | E
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |650 < X ≤ 800
| + | |
| - | |475 < X ≤ 600
| + | |
| - | |500 < X ≤ 625
| + | |
| - | |400 < X ≤ 500
| + | |
| - | |215 < X ≤ 260
| + | |
| - | |475 < X ≤ 600
| + | |
| - | |800 < X ≤ 950
| + | |
| - | |275 < X ≤ 350
| + | |
| - | |1250 < X ≤ 1500
| + | |
| - | |800 < X ≤ 950
| + | |
| - | |1250 < X ≤ 1500
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | F
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |800 < X ≤ 950
| + | |
| - | |600 < X ≤ 725
| + | |
| - | |625 < X ≤ 750
| + | |
| - | |500 < X ≤ 600
| + | |
| - | |260 < X ≤ 305
| + | |
| - | |600 < X ≤ 725
| + | |
| - | |950 < X ≤ 1100
| + | |
| - | |350 < X ≤ 425
| + | |
| - | |1500 < X ≤ 1750
| + | |
| - | |950 < X ≤ 1100
| + | |
| - | |1500 < X ≤ 1750
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | G
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |X > 950
| + | |
| - | |X > 725
| + | |
| - | |X > 750
| + | |
| - | |X > 600
| + | |
| - | |X > 305
| + | |
| - | |X > 725
| + | |
| - | |X > 1100
| + | |
| - | |X > 425
| + | |
| - | |X > 1750
| + | |
| - | |X > 1100
| + | |
| - | |X > 1750
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | |}<br/>
| + | |
| - | '''Table 5: Classification for the water ratio 2'''<br/>
| + | |
| | | | |
| - | '''8.2 Conversion Factors and their Sources'''<br/> | + | ===<u>'''General conversion factors'''</u>=== |
| | | | |
| - | <u>'''General conversion factors:'''</u><br/>
| + | [[Image:Wood.jpg]]<br/> |
| | | | |
| - | {| align="center" style="background-color:#C0E0F0"
| + | ===<u>'''Conversion factors for final energy use'''</u>=== |
| - | |-
| + | [[Image:Natgaz.jpg]]<br/> |
| - | ! scope=col |Energy or energy source
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col |Type of conversion
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col |Conversion factor
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col |Unit
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row |
| + | |
| - | |MWh to kWh
| + | |
| - | |1000
| + | |
| - | |kWh/MWh
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row |
| + | |
| - | |kWh to MWh
| + | |
| - | |0,001
| + | |
| - | |MWh/kWh
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row |wood (logs)
| + | |
| - | |kg to kWh
| + | |
| - | |4,3
| + | |
| - | |kWh/kg
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | Wood (chips)
| + | |
| - | |kg to kWh
| + | |
| - | |3,3
| + | |
| - | |kWh/kg
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | Wood(pellets)
| + | |
| - | |kg to kWh
| + | |
| - | |4,9
| + | |
| - | |kWh/kg
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | Anthracite
| + | |
| - | |kg to kWh
| + | |
| - | |8,6
| + | |
| - | |kWh/kg
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | Brown coal
| + | |
| - | |kg to kWh
| + | |
| - | |5,4
| + | |
| - | |kWh/kg
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | Fuel oil (light)
| + | |
| - | |l to kWh
| + | |
| - | |10,0
| + | |
| - | |kWh/l
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | Natural gas
| + | |
| - | |m3 to kWh
| + | |
| - | |10,1
| + | |
| - | |kWh/m3
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | Natural gas
| + | |
| - | |UHV to LHV
| + | |
| - | |0,9
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | Biogas
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |6,0
| + | |
| - | |kWh/m3
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | Liquified gas
| + | |
| - | |m3 to kWh
| + | |
| - | |26,0
| + | |
| - | |kWh/m3
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | Liquified gas
| + | |
| - | |kg to kWh
| + | |
| - | |12,9
| + | |
| - | |kWh/kg
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | Liquified gas
| + | |
| - | |UHV to LHV
| + | |
| - | |0,9
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | |}<br/>
| + | |
| - | '''Table 7: General conversion factors'''<br/> | + | |
| | | | |
| - | <u>'''Conversion factors for final energy use:'''</u><br/> | + | ===<u>'''Conversion factors for generation of electricity (average national electricity production)'''</u>=== |
| - | {| align="center" style="background-color:#C0E0F0"
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Energy or energy source
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Conversion factor final energy to primary energy[kWh/kWh]
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Type of conversion factor
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Conversion factor final energy to CO2 equivalents[kg/kWh]
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Source
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | Natural gas
| + | |
| - | | 1,17
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,2537 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | Liquified gas
| + | |
| - | | 1,16
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,2763 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | Biogas
| + | |
| - | | 1,14
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,2500
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | Fuel oil (light)
| + | |
| - | | 1,19
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,3199 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | Anthracite
| + | |
| - | | 1,11
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,4397 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | Brown coal
| + | |
| - | | 1,25
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,4579 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | Wood (logs)
| + | |
| - | | 1,04
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,0213 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | Wood (Chips)
| + | |
| - | | 1,10
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,0268 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | Wood (pellets)
| + | |
| - | | 1,13
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,0349 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | Solar Thermal collector
| + | |
| - | | 1,17
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,0479 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | |}<br/>
| + | |
| - | '''Table 8: Conversion factors for final energy use'''<br/>
| + | |
| | | | |
| - | <u>'''Conversion factors for generation of electricity
| + | [[Image:Table7 conversion factors Energy CO2.jpg]]<br/> |
| - | (average national electricity production):'''</u><br/>
| + | |
| | | | |
| - | {| align="center" style="background-color:#C0E0F0"
| + | ===<u>'''Conversion factors for generation of electricity (specified energy sources)'''</u>=== |
| - | |-
| + | '''Conversion factors for generation of electricity'''<br/> |
| - | ! scope=col | Country code
| + | [[Image:Enrsources.jpg]]<br/> |
| - | ! scope=col | Conversion factor final energy to primary energy[kWh/kWh]
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Type of conversion factor
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Conversion factor final energy to CO2 equivalents[kg/kWh]
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Source
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | AT
| + | |
| - | | 1,69
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,2388 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | BE
| + | |
| - | | 3,26
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,3102 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row |CY
| + | |
| - | | 3,37
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,9470 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row |CZ
| + | |
| - | | 3,01
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,9076 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row |DE
| + | |
| - | | 2,90
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,6249 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row |DK
| + | |
| - | | 2,56
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,6787 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row |EE
| + | |
| - | | 2,85
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 1,0113 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row |ES
| + | |
| - | | 2,59
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,4914 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row |FI
| + | |
| - | | 3,36
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,4022 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row |FR
| + | |
| - | | 3,32
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,1080 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row |GR
| + | |
| - | | 2,62
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,8812 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row |HU
| + | |
| - | | 3,59
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,6910 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row |HR
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row |IE
| + | |
| - | | 2,44
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,7029 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row |IT
| + | |
| - | | 2,31
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,5633 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row |LT
| + | |
| - | | 3,68
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,3646 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row |LU
| + | |
| - | | 2,75
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,3683 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | LV
| + | |
| - | | 2,42
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,4401 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | MT
| + | |
| - | | 3,38
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,9491 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | NL
| + | |
| - | | 2,69
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,6174 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | PL
| + | |
| - | | 2,70
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 1,0185 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | PT
| + | |
| - | | 2,52
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,6284 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | SE
| + | |
| - | | 2,17
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,0758 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | SI
| + | |
| - | | 2,47
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,3905 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | SK
| + | |
| - | | 3,10
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,3779 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | UK
| + | |
| - | | 2,66
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,5556 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | NO
| + | |
| - | | 1,04
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,0145 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | CH
| + | |
| - | | 2,06
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,0405 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | BG
| + | |
| - | | 3,11
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,5521 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | RO
| + | |
| - | | 2,64
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,6400 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | TR
| + | |
| - | | 2,50
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,6142 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | |}<br/>
| + | |
| - | '''Table 9: Conversion factors for generation of electricity''' | + | |
| | | | |
| - | <u>'''Conversion factors for generation of electricity (specified energy sources):'''</u><br/>
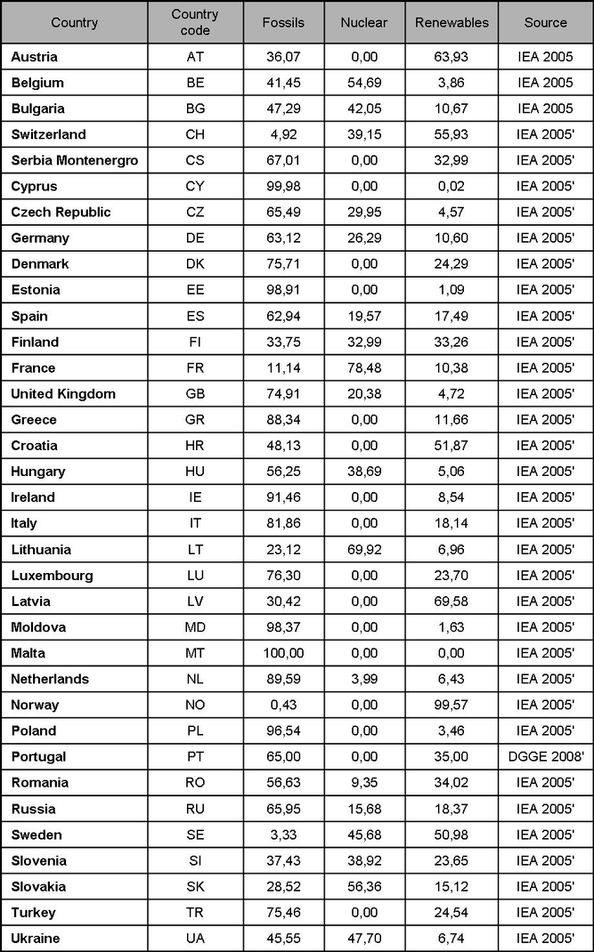
| + | '''Energy mix by country'''<br/> |
| - | {| align="center" style="background-color:#C0E0F0"
| + | [[Image:Table_8__Energy_Mix_2005_en_actu.jpg]]<br/> |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Energy or energy source
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Conversion factor final energy to primary energy[kWh/kWh]
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Type of conversion factor
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Conversion factor final energy to CO2 equivalents[kg/kWh]
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Source
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | monocrystalline PV cell
| + | |
| - | | 1,62
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,1660 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | electricity (green, mix water 50 %/wind 50 %)
| + | |
| - | | 1,05
| + | |
| - | | KEVnonrenewable+renewable
| + | |
| - | | 0,0295 GEMIS 4.3 2004
| + | |
| - | | Öko-Institut
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | |}<br/>
| + | |
| - | '''Table 10: Conversion factors for generation of electricity'''<br/>
| + | |
| | | | |
| - | <u>'''Conversion factors for district heat (used by default):'''</u><br/> | + | ===<u>'''Conversion factors for district heat (used by default)'''</u>=== |
| - | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center; width:80%; number-align:center; style="background-color:#C0E0F0"
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Conversion factor final energy to primary energy[kWh/kWh]
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Type of conversion factor
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Conversion factor final energy to CO2 equivalents[kg/kWh]
| + | |
| - | ! scope=col | Source
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | District heat, produced in a cogeneration plant 0,78
| + | |
| - | | CEDtotal
| + | |
| - | | 0,24
| + | |
| - | | GEMIS version 4.14 calculation made by the IWU, 2004, 70 % cogeneration
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | ! scope=row | District heat, not produced in a cogeneration plant 1,49
| + | |
| - | | CEDtotal
| + | |
| - | | 0,41
| + | |
| - | | GEMIS version 4.14 calculation made by the IWU, 2004
| + | |
| - | |-
| + | |
| - | |}<br/>
| + | |
| - | '''Table 11: Conversion factors for district heat''' <br/>
| + | |
| | | | |
| - | '''8.3 Glossary'''<br/>
| + | [[Image:Primaryener.jpg]]<br/> |
| - | | + | |
| - | '''CO2 emission factor'''<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | The CO2 emission factor is the sum of all the CO2 emissions linked to the production and usage of a product.<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | '''CO2 emissions'''<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | To simplify the term “greenhouse gas emissions measured in kg of CO2 equivalents” the term “CO2 emissions” is used as an equivalent in this users’ guide.<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | '''CO2 equivalents'''<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | CO2 equivalents are a metric measure used to compare the emissions from various greenhouse gases based upon their global warming potential (GWP). Carbon dioxide equivalents are commonly expressed as “million metric tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalents (MMTCDE)”. The carbon dioxide equivalent for a gas is derived by multiplying the tonnes of the gas by the associated GWP. MMTCDE = (million metric tonnes of a gas) x (GWP of the gas). For example, the GWP for methane is 21 and for nitrous oxide 310. This means that emissions of one million metric tonnes of methane and nitrous oxide respectively is equivalent to emissions of 21 and 310 million metric tonnes of carbon dioxide. On the Display® poster the emissions are shown in kilogrammes of CO2 equivalents.<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | '''CO2 ratio'''<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | The CO2 ratio describes the emission of greenhouse gases expressed in CO2 equivalents per square metre of the internal gross floor area of the building and per year.<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | '''Cogeneration plant'''<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | A cogeneration plant is a thermal power station in which all the steam generated in the boilers passes to turbo-generators for electricity generation, but designed so that steam may be extracted at points on the turbine and/or from the turbine exhaust as back-pressure steam and used to supply heat.<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | '''Cumulative energy demand (CED) factor'''<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | The CED factor is defined in the German guideline VDI 4600 and is equal to the sum of all primary energy inputs of a product or a service. This contains its production, usage, and disposal. It contains not only the energy demand of the process necessary to provide a service or to produce a product but also the energy that remains in a product, e.g. the lower heating value of mineral oil in plastic products.<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | '''Cumulative energy use factor'''<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | The cumulative energy use factor describes the overall primary energy consumption which is linked with the creation or use of a product or a service, including all preproduction chains but without primary energy used as materials such as mineral oil in plastic products. Furthermore, the energy utilised for the disposal is not taken into account. Since there is not a widely used abbreviation for this factor in English so far we use the German abbreviation KEV in this users’ guide.<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | '''Efficiency'''<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | Efficiency is defined as the ratio of the energy output to the energy input of a machine.<br/>
| + | |
| - |
| + | |
| - | '''Final energy'''<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | (also: energy supplied) Final energy is the part of the secondary energy that is available to the consumer. It equals the secondary energy less losses such as transmission and transformation losses and is finally converted into useful energy.<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | '''Greenhouse gases'''<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | Greenhouse gases are gaseous pollutants released into the atmosphere through the burning of fossil fuels and through other avenues, which amplify the greenhouse effect. The Kyoto protocol includes the following greenhouse gases: Carbon dioxide (CO2), Methane (CH4), Nitrous oxide (N2O), Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), Perfluorocarbons (PFCs), and Sulphur hexafluoride (SF6).<br/>
| + | |
| - |
| + | |
| - | '''Gross internal floor area'''<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | The gross internal floor area of a building is the area measured to the internal face of the perimeter wall at each floor level. It includes areas occupied by internal walls and partitions, columns, piers and other internal projections, internal balconies, stairwells, toilets, lift lobbies, fire corridors, atria measured at base level only, and covered plant rooms. It excludes the perimeter wall thickness and external projections, external balconies and external fire escapes. Furthermore, unused areas such as unheated cellars or lofts are not included in the gross internal floor area. Its unit is m².<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | '''Lower heating value (LHV)'''<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | (also: net calorific value, lower calorific value, net heating value) The lower heating value is the total heat produced on the complete combustion of a fuel less the energy in the uncooled products of combustion. Among these is uncondensed water vapour.<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | '''Primary energy'''<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | Primary energy is the energy that has not been subjected to any conversion or transformation process. It is contained in fossil fuels and energy derived from renewable sources such as the sun, wind and waves. All the energy which we use comes from these primary sources, though very often the energy may be supplied in the form of secondary fuels such as electricity, manufactured gas, or coke. <br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | '''Primary energy ratio'''<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | The primary energy ratio describes the consumption of primary energy per square metre of the internal gross floor area of the building and per year.<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | '''Secondary energy'''<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | Secondary energy is the energy produced by the conversion of primary energy, e. g. electricity, hydrogen, or petrol.<br/>
| + | |
| - | '''
| + | |
| - | Upper heating value (UHV)'''<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | (also: gross calorific value, higher calorific value) The higher heating value of a fuel is the total heat developed after the products of a complete combustion are cooled to the original fuel temperature.<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | '''Useful energy'''<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | Useful energy is the portion of final energy which is actually available after final conversion to the consumer for the respective use. In final conversion, electricity becomes for instance light, mechanical energy or heat.<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | '''Water ratio'''<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | For the main cases, the water ratio describes the consumption of water per square metre of the internal gross floor area of the building and per year. For swimming pools, it’s more pertinent to speak about water consumption per swimmer/user.<br/>
| + | |
| - |
| + | |
| - | '''Weather correction factor'''<br/>
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | The weather correction factor is supposed to take into account the climatic difference between the year your data is from and an average year. Please note that this factor does not take into account climatic differences between two different climatic zones.
| + | |
The Danish classification, used since 1996, is the base of the Display® classification schemes. So far the Danish scheme, taking into account a building typology, is the only classification all over Europe.
By increasing the number of registered buildings in the different types and considering the recommendations of the CEN (Normalization European Comity), an iterative approach allowed to adjust the classification schemes after the first 6 test months.
Furthermore, the classification scheme will take into account the information provided by the Concerted Action, a working group composed of representatives from nearly all EU member states. The objective of the CA working group is the harmonisation of the implementation of the Energy Performance of Buildings Directive.
Currently, 11 types of buildings can be classified. The classification scheme could change in the future.